Choosing your first microcontroller board can be overwhelming, especially when two of the most popular options—ESP32 and Raspberry Pi Pico—offer strong features, affordable pricing, and active communities. If you're a beginner looking to learn embedded C, experiment with wireless projects, or build simple embedded systems, both boards are excellent choices.
However, they shine in different areas. This guide breaks down the differences, strengths, and ideal use cases to help you choose the right one.

1. Overview: ESP32 vs Raspberry Pi Pico—What Are the Key Differences?
ESP32 Overview: Wireless-Ready Microcontroller
The ESP32 is widely known for integrating Wi-Fi and Bluetooth into a compact, low-cost microcontroller. It’s ideal for IoT, automation, remote monitoring, wireless communication, and multitasking. It supports multiple development environments including Arduino IDE, PlatformIO, and the powerful ESP-IDF.
Raspberry Pi Pico Overview: Dual-Core ARM MCU with Excellent Documentation
Raspberry Pi Pico (and the Pico W version) focuses on clean architecture, predictable timing, and a traditional ARM Cortex-M0+ environment. The Pico W now officially supports both Wi-Fi and low-power Bluetooth (Bluetooth LE) after a 2023 firmware update. However, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth share the same antenna, so high-bandwidth Wi-Fi and Bluetooth cannot operate simultaneously. Pico is especially popular among those learning low-level embedded systems, C programming, and assembly.

Quick Comparison
• Wireless: ESP32 (Wi-Fi + BLE), Pico W (Wi-Fi + BLE)
• Architecture: ESP32 (Xtensa / RISC-V), Pico (ARM Cortex-M0+)
• Best For: ESP32 (IoT), Pico (Low-level embedded learning)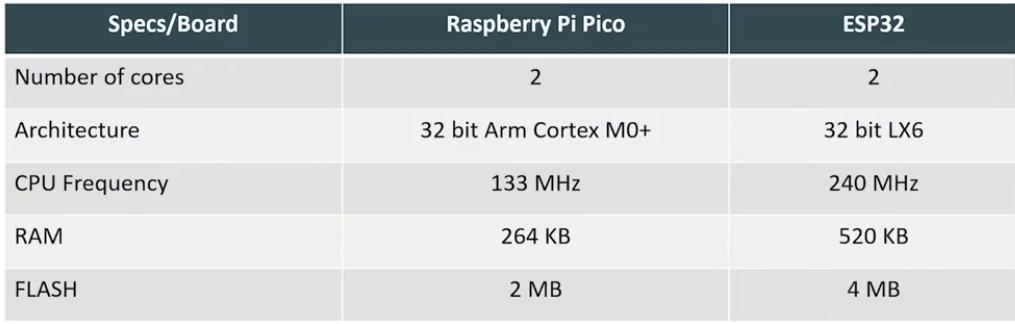
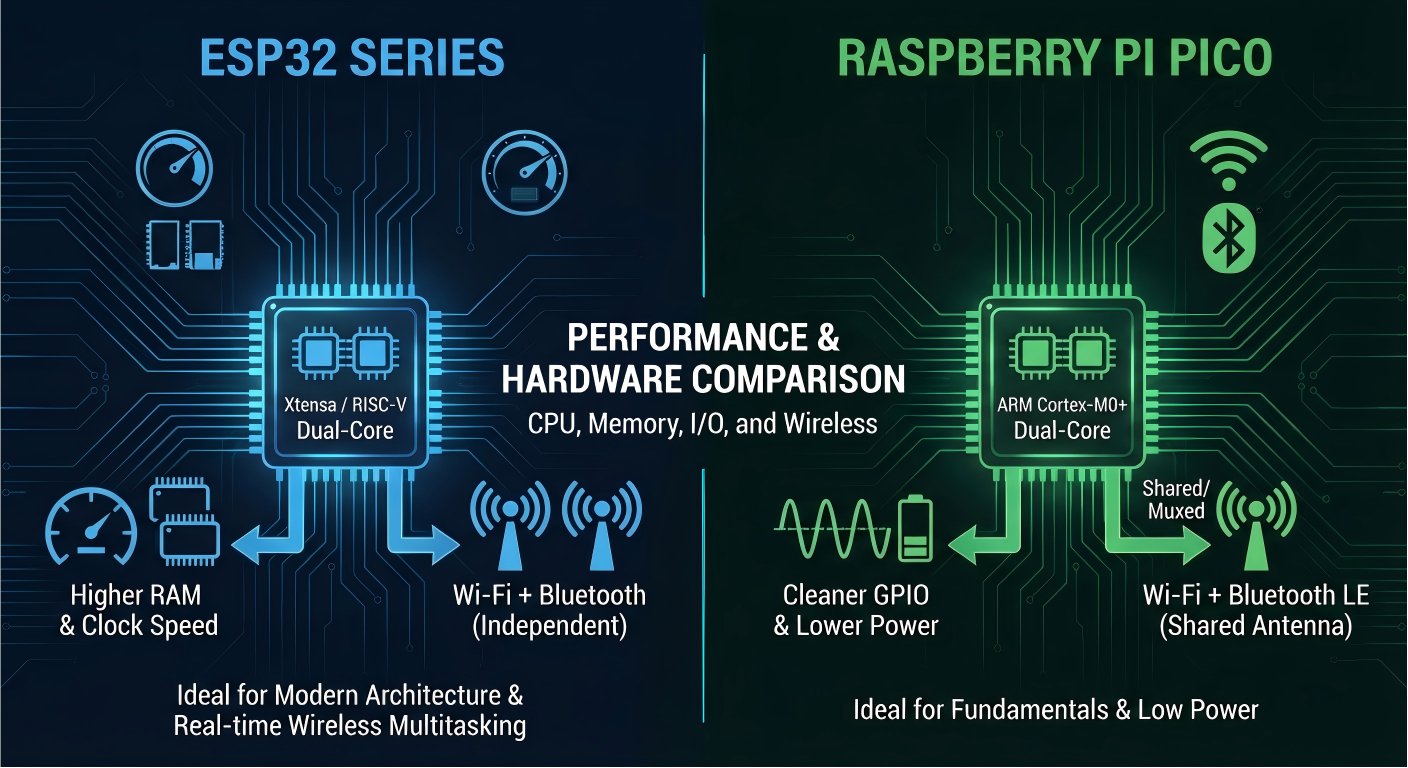
2. Performance and Hardware Comparison
CPU Architecture: Xtensa/RISC-V vs ARM Cortex-M0+
• ESP32 typically uses dual-core Xtensa CPUs, while newer ESP32-C series use RISC-V—excellent for learning modern embedded architecture.
• Raspberry Pi Pico’s dual-core ARM Cortex-M0+ is simpler but extremely well documented, making it ideal for learning fundamentals.
Memory, Clock Speed & GPIO
• ESP32 offers more RAM and higher clock speeds.
• Pico provides cleaner GPIO timing and lower power consumption.
Wireless Capabilities
• ESP32: Wi-Fi + Bluetooth
• Pico W: Wi-Fi + Bluetooth LE (shared antenna, cannot do high-bandwidth Wi-Fi + BLE simultaneously)
If wireless versatility is important, ESP32 still has a slight edge in real-time multitasking wireless applications.
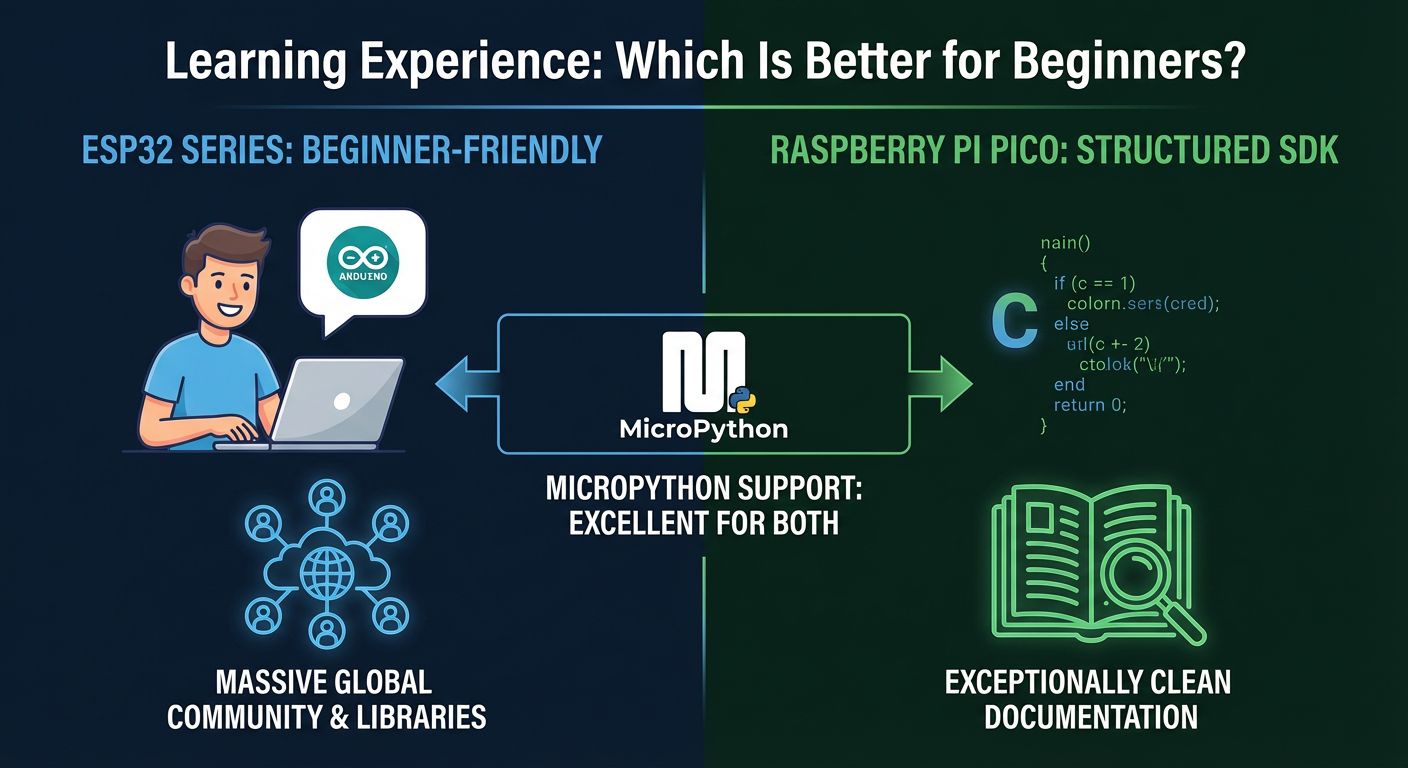
3. Learning Experience: Which Is Better for Beginners?
Ease of Programming
• ESP32: Very beginner-friendly through Arduino IDE; advanced users can use ESP-IDF.
• Pico: Requires using the Pico SDK for C, which is more “traditional” embedded programming.
MicroPython Support
Both boards support MicroPython well, making them excellent choices for lightweight scripting and quick prototyping.
Documentation & Community
• ESP32 has a massive global community, extensive tutorials, and years of libraries.
• Raspberry Pi Pico offers exceptionally clean documentation and structured SDK references.
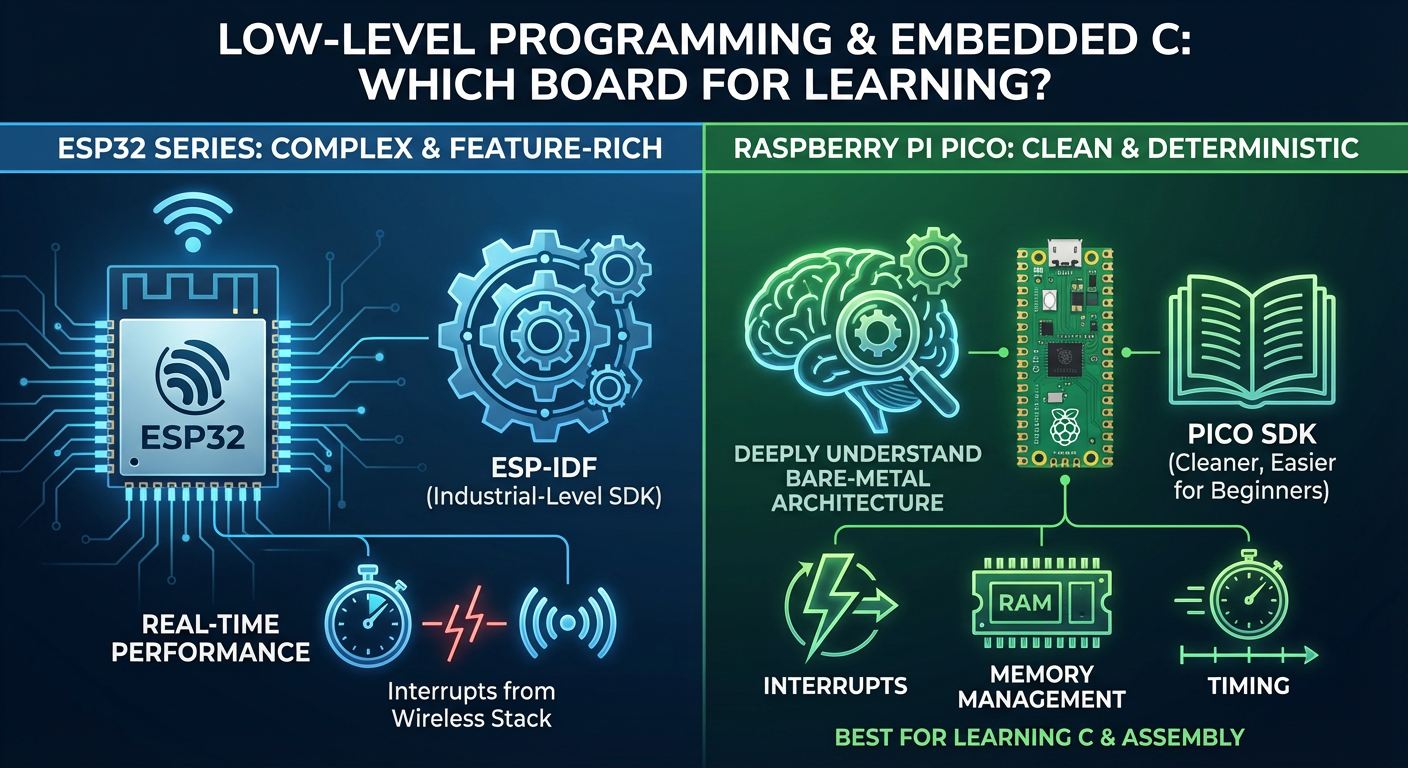
4. Low-Level Programming & Embedded C
Which Board Is Better for Learning C and Assembly?
If your goal is to deeply understand:
• interrupts
• memory management
• timing
• bare-metal architecture
Raspberry Pi Pico is the stronger choice.
SDK Comparison
• ESP-IDF: Feature-rich, powerful, industrial-level, but complex.
• Pico SDK: Cleaner, easier for beginners, great for embedded C and ARM basics.
Real-Time Performance
For deterministic timing, Pico performs better because it doesn’t run a wireless stack that interrupts execution.
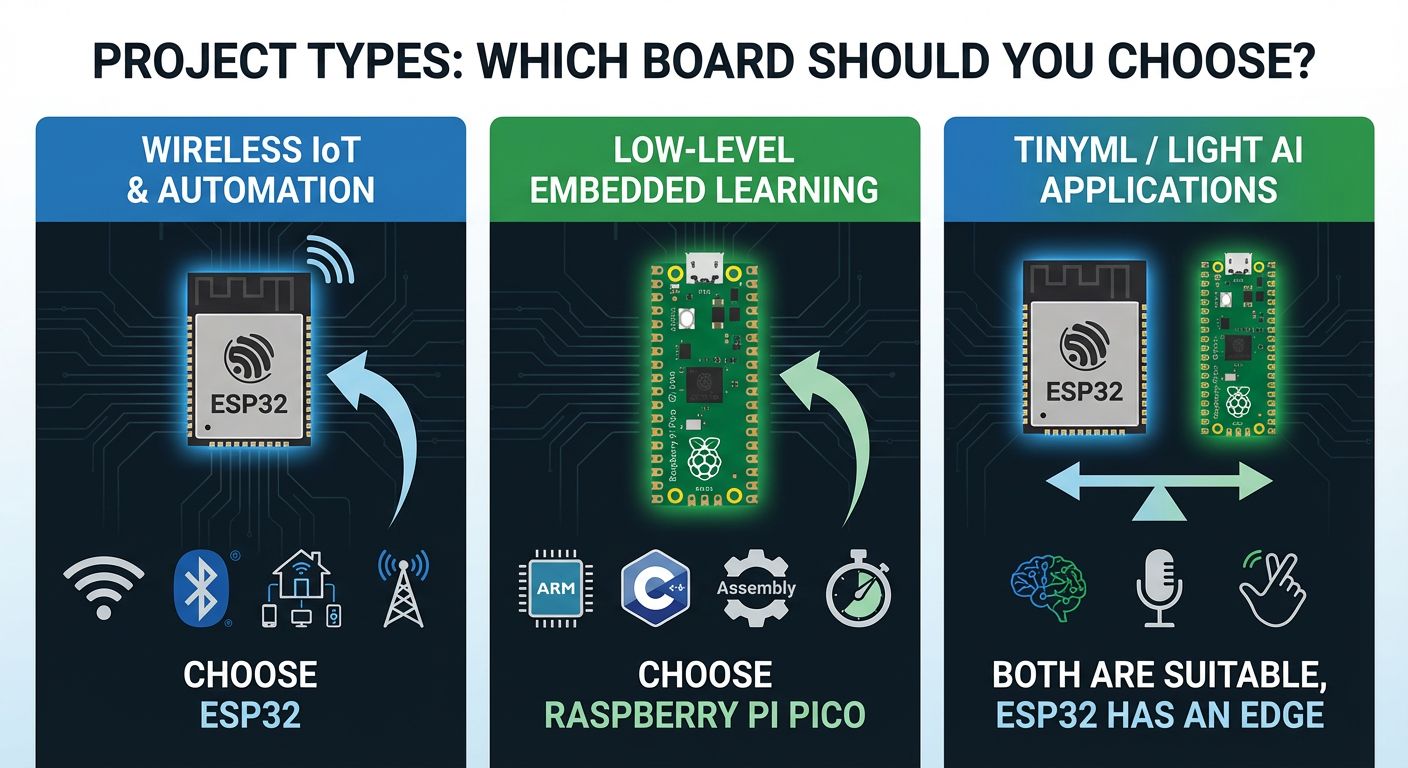
5. Project Types: Which Board Should You Choose?
For Wireless IoT & Automation
Choose ESP32 if your project uses:
• Wi-Fi
• Bluetooth
• Home automation
• Remote sensing
• Smart devices
For Low-Level Embedded Learning
Choose Raspberry Pi Pico if you want to learn:
• ARM architecture
• Embedded C
• Assembly
• Timing-sensitive design
For TinyML / Light AI Applications
Both ESP32 and Pico are suitable for TinyML (microcontroller-scale machine learning). Examples include:
• Keyword spotting / voice wake-up
• Sensor anomaly detection
• Simple image or gesture classification
ESP32 is generally better for TinyML due to higher processing power, more memory, and richer libraries. However, neither board can handle large-scale AI models.
For Mixed Systems
Some advanced setups combine both:
• Raspberry Pi (Linux SBC) as the main controller
• ESP32 or Pico as low-level sensor nodes
6. Price, Availability & Ecosystem
Board Cost Comparison
In many countries:
• ESP32 ≈ $5
• Pico W ≈ $8
ESP32 offers more features per dollar, especially for wireless and TinyML applications.
Libraries & Toolchains
Both ecosystems are strong, but ESP32 has more Wi-Fi/BLE and TinyML libraries, while the Pico SDK is better structured for embedded learning.
Long-Term Community Support
Both are safe choices with strong manufacturer support.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Is ESP32 better than Raspberry Pi Pico for beginners?
• If you want wireless projects and easy programming → ESP32
• If you want to learn embedded C and fundamentals → Pico
Can Raspberry Pi Pico or ESP32 handle AI?
• They cannot run complex AI models, but both are excellent for TinyML applications such as voice wake-up or sensor data analysis. ESP32 has more capability in this area.
Which is better for battery-powered low-power projects?
• Raspberry Pi Pico generally performs better at ultra-low-power operation.
8.Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
• Wireless IoT + fast prototyping → Get ESP32
• Embedded C, real-time control, ARM learning → Get Raspberry Pi Pico
For long-term learning, having both is ideal—and many advanced engineers use them together in larger systems.
Related Products