Many users have experienced this: two USB ports look exactly the same, but the transfer speeds are completely different. A USB Type-C port on one laptop may deliver 10Gbps, while another Type-C port barely reaches USB 2.0 speeds.
Why does this happen?
This updated guide explains USB speed differences, the real meaning of USB standards, and how to identify the true speed of your USB ports and cables.
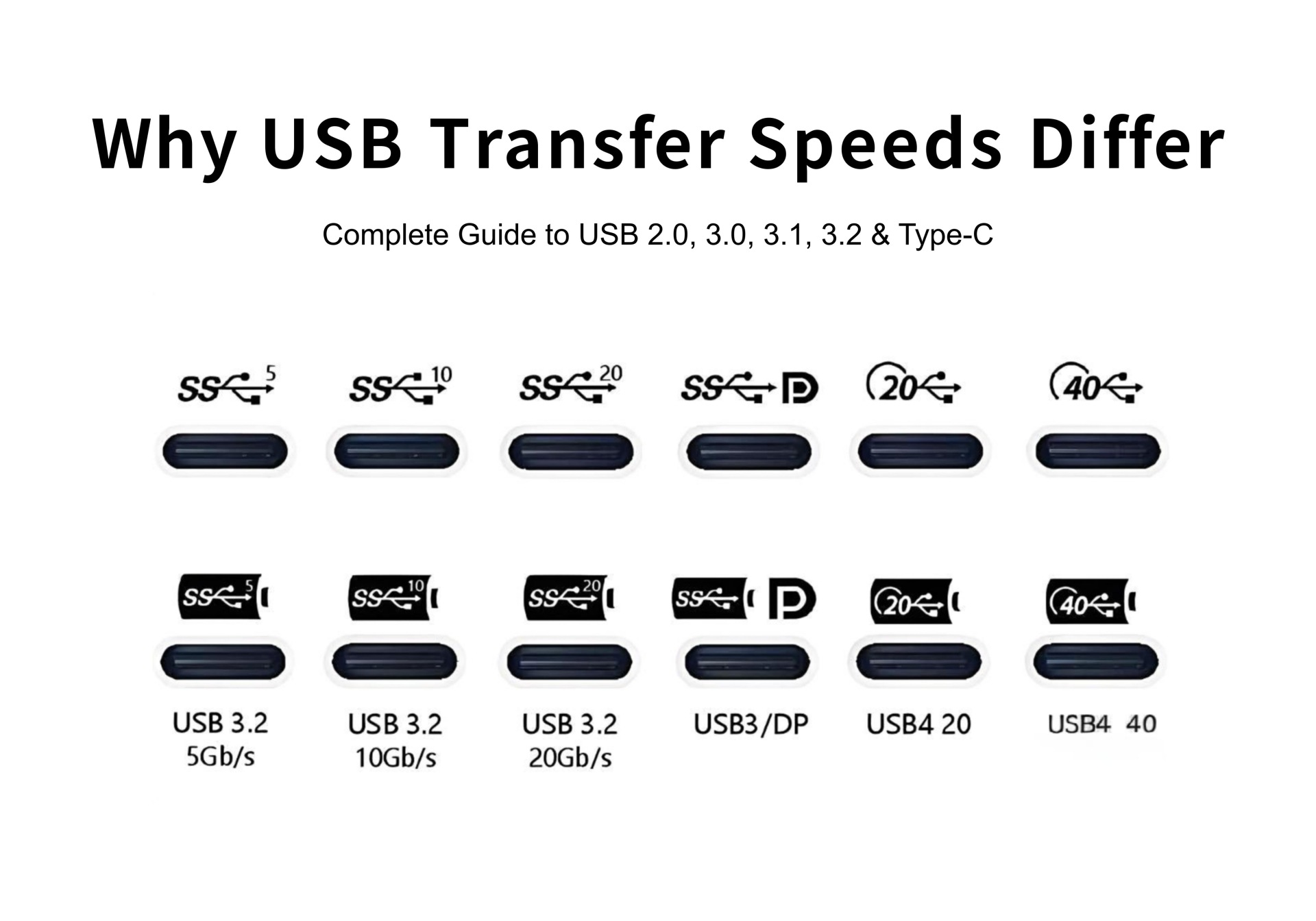
1. Why USB Ports Have Different Transfer Speeds
Even when the connector looks identical, USB performance varies because:
• Different generations of USB standards
• Different internal transmission lanes
• Manufacturer-specific function limitations
• Cable quality and supported protocols
• Device controller chip capability
In short: same connector ≠ same speed.
2. USB Standards Explained: From USB 2.0 to the Latest USB 3.2
USB standards have changed significantly, and naming updates have made things even more confusing.
USB 2.0 – 480 Mbps
Suitable for mouse, keyboard and basic storage.
USB 3.2 Gen 1 (formerly USB 3.0 / USB 3.1 Gen 1) – 5 Gbps
The "blue" USB-A port commonly seen on PCs.
USB 3.2 Gen 2 (formerly USB 3.1 Gen 2) – 10 Gbps
Double the speed of Gen 1.
USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 – 20 Gbps
Uses dual-lane transmission, supported only on certain Type-C ports.
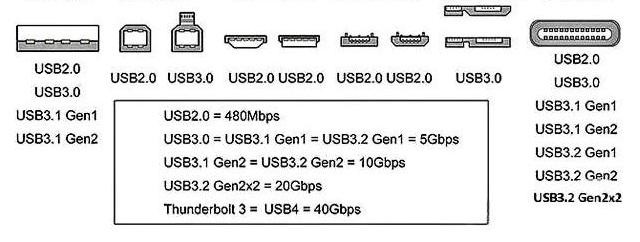
2025 Updated USB Speed Table
|
USB Standard |
Old Name |
Speed |
Real Transfer Rate (Approx.) |
|
USB 2.0 |
— |
480 Mbps |
~35–40 MB/s |
|
USB 3.2 Gen 1 |
USB 3.0 / 3.1 Gen1 |
5 Gbps |
~450–500 MB/s |
|
USB 3.2 Gen 2 |
USB 3.1 Gen2 |
10 Gbps |
~900–1100 MB/s |
|
USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 |
— |
20 Gbps |
~2000 MB/s |
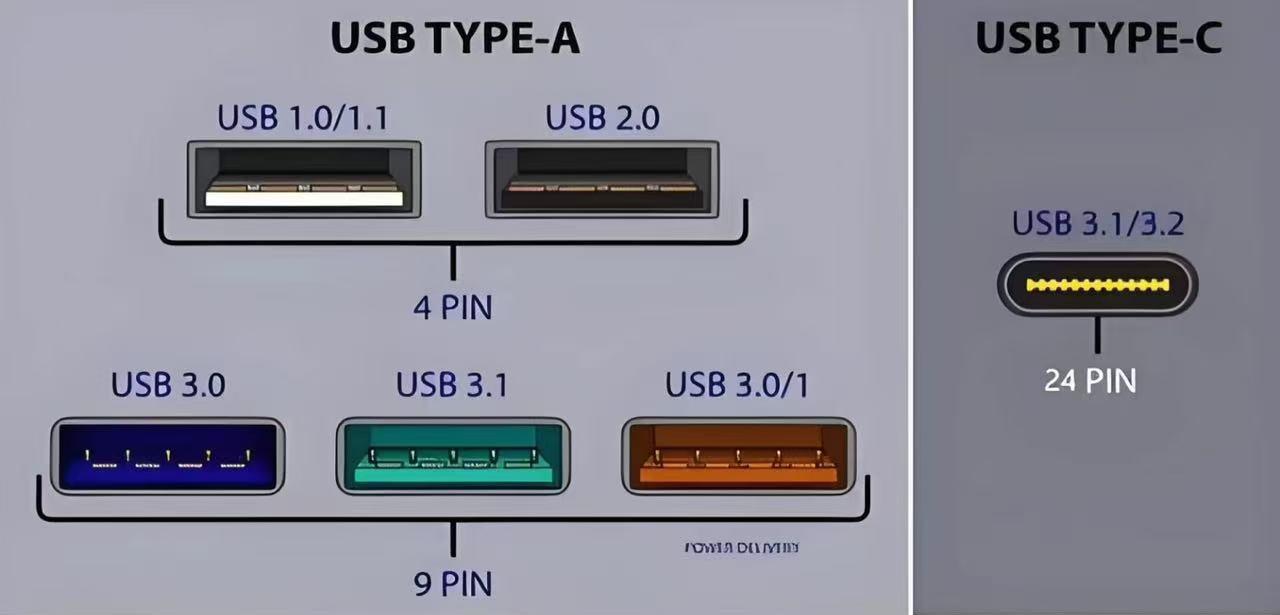
3. USB Type-C vs USB Speed Standards: The Most Common Misunderstanding
• USB 2.0
• USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5Gbps)
• USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gbps)
• USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 (20Gbps)
• Thunderbolt 3/4
• DisplayPort
• Power Delivery (PD)
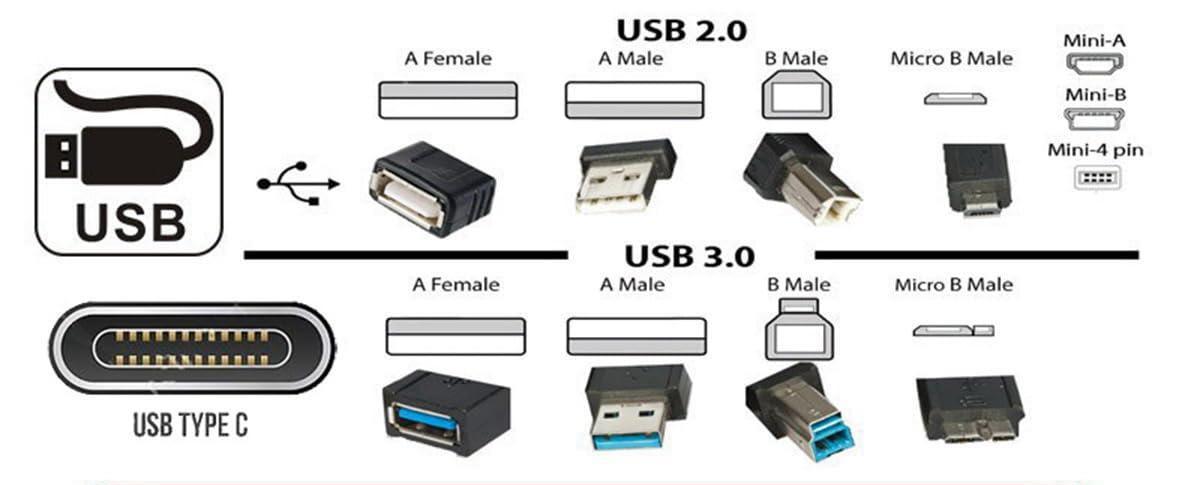

4. How to Identify the Real Speed of a USB Port or Cable
a. Check your system information
• Windows: Device Manager → Universal Serial Bus Controllers
• macOS: System Information → USB
Look for:
• USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5Gbps)
• USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gbps)
• USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 (20Gbps)
b. Look for physical symbols
• SS (SuperSpeed) = USB 3.x
• SS10 = 10Gbps
• SS20 = 20Gbps
• Thunderbolt symbol = 40Gbps

c. Cable quality matters
Cheap cables often support only USB 2.0, even with Type-C connectors.
d. Actual transfer test
Fast SSD should exceed:
• 450 MB/s → USB 3.2 Gen 1
• 900 MB/s → USB 3.2 Gen 2
e. Check manufacturer specifications
Especially important for laptops and USB hubs.

5. FAQ: Common Questions About USB Transfer Speeds
Because it may only support USB 2.0 or USB 3.2 Gen 1.
No. Thunderbolt uses a Type-C connector but supports much higher bandwidth (up to 40Gbps).
Yes. Longer, low-quality cables cause signal degradation.
Blue often indicates USB 3.0, but not always reliable.
6. High-Quality USB Connectors & Cables from Elecbee
If you are looking for certified high-speed connectors or custom cable assemblies, feel free to contact us anytime.







