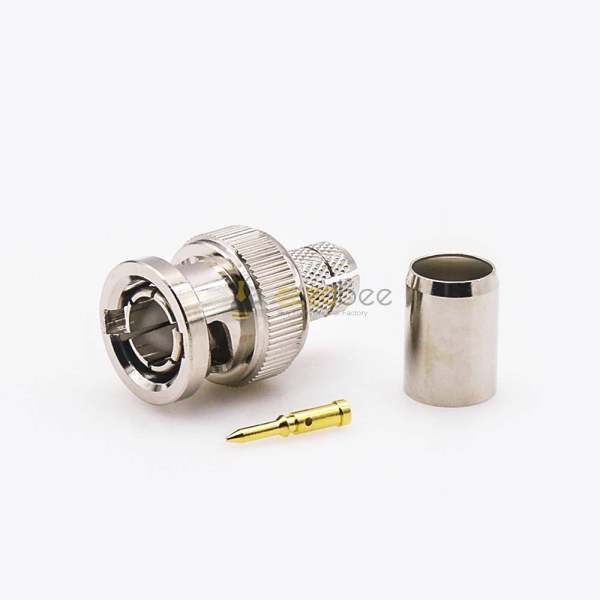
BNC and TNC connectors are two commonly used RF connectors in communication and microwave systems. Although they look similar and share the same Neill–Concelman design origin, their performance and application scenarios are quite different. Understanding the difference between BNC and TNC connectors helps engineers and buyers choose the right solution for their projects.

1.What Are BNC and TNC Connectors?
The BNC connector was invented in the 1940s and features a bayonet-style snap-on coupling. It allows quick connection and disconnection, making it ideal for test equipment and indoor applications. BNC connectors are available in 50 ohm and 75 ohm versions and typically support frequencies up to 11 GHz under ideal conditions.
The TNC connector, invented in the 1950s, is a threaded version of the BNC connector. Its full name is Threaded Neill–Concelman. The threaded coupling was designed to overcome the performance limitations of BNC connectors at higher frequencies and in environments with vibration.
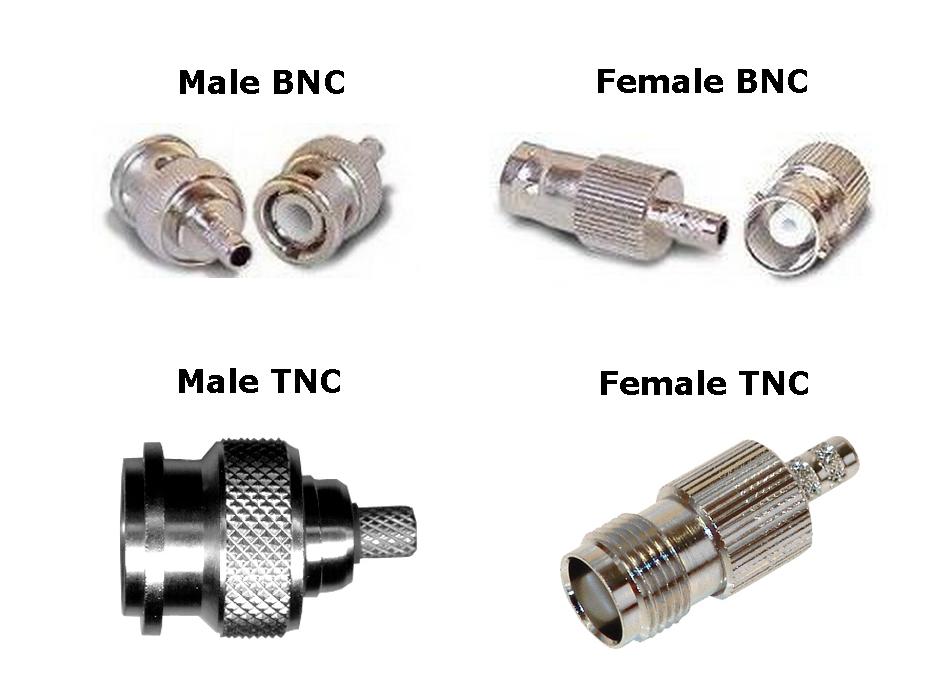

2.BNC vs TNC Connector: Key Differences Explained
|
Feature |
BNC Connector |
TNC Connector |
|
Coupling Type |
Bayonet (snap-on) |
Threaded |
|
Locking Strength |
Moderate |
Strong |
|
Vibration Resistance |
Low |
High |
|
Typical Impedance |
50 Ω / 75 Ω |
50 Ω |
|
Size |
Compact |
Slightly larger |
The most obvious difference between BNC and TNC connectors is the connection mechanism. The threaded design of TNC provides a more secure and stable connection, especially in high-frequency or high-vibration environments.
3.Frequency Range and Performance Comparison
While both BNC and TNC connectors are often rated up to DC–11 GHz, their real-world performance differs:
• BNC connectors may suffer from signal leakage and micro-movement at microwave frequencies.
• TNC connectors maintain better impedance stability and lower VSWR due to the threaded coupling.
For applications above several GHz or in outdoor environments, TNC connectors generally offer more reliable performance.
4.BNC vs TNC Applications: When to Use Each
Common BNC connector applications:
• Test and measurement equipment
• Broadcast systems (75 Ω)
• Computers and LANs
• Medical equipment
• Cable modems
• Base stations (indoor)

5.Common TNC connector applications:
• Antennas and wireless systems
• Industrial and outdoor equipment
• Aerospace
• Broadband communication
• High-vibration environments

6.Are BNC and TNC Connectors Interchangeable?
Although BNC and TNC connectors look similar, they are not directly interchangeable due to different coupling mechanisms. Adapters are available, but using adapters may introduce signal loss and is not recommended for high-frequency or precision applications.
7.How to Choose Between BNC and TNC Connectors
Choose BNC connectors if you need:
• Fast connect/disconnect
• Indoor or lab environments
• Lower-frequency applications
Choose TNC connectors if you need:
• Better high-frequency performance
• Resistance to vibration
• Outdoor or industrial reliability
8.Final Thoughts
The difference between BNC and TNC connectors lies mainly in connection type, performance stability, and application environment. By understanding these factors, you can confidently select the right RF connector for your system.
Elecbee specializes in RF connectors, USB connectors, and cable assemblies with over 13 years of manufacturing experience. If you need help selecting the right BNC or TNC connector, feel free to contact us or explore our product range directly.

Related Products
• BNC connectors
• TNC connectors
• RF Coaxial Connectors
• USB connectors
• Cable assemblies







