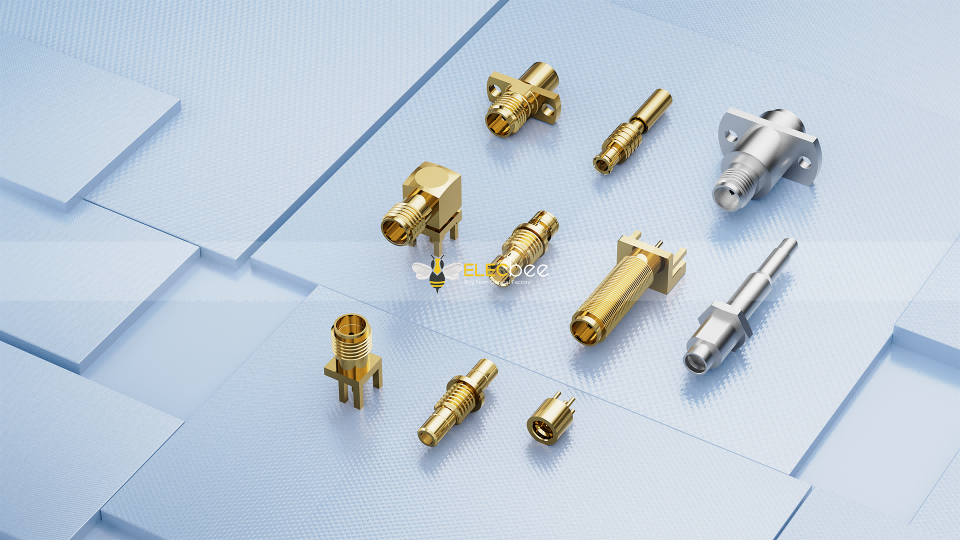
Selecting the right RF connector is critical for achieving stable signal transmission, low loss, and long-term system reliability. With dozens of RF connector types available—BNC, SMA, TNC, N-type, MCX/MMCX, and more—the best choice depends on your application, frequency, installation method, and mechanical requirements.
This guide provides a complete, updated overview of RF connector types, technical parameters, materials, and a step-by-step method to help you choose the right connector for 2025-era wireless, communication, and industrial systems.

1.What Is an RF Connector? (Quick Overview)
An RF connector is a specialized coaxial interface designed to maintain controlled impedance, minimize signal reflection, and support high-frequency transmission.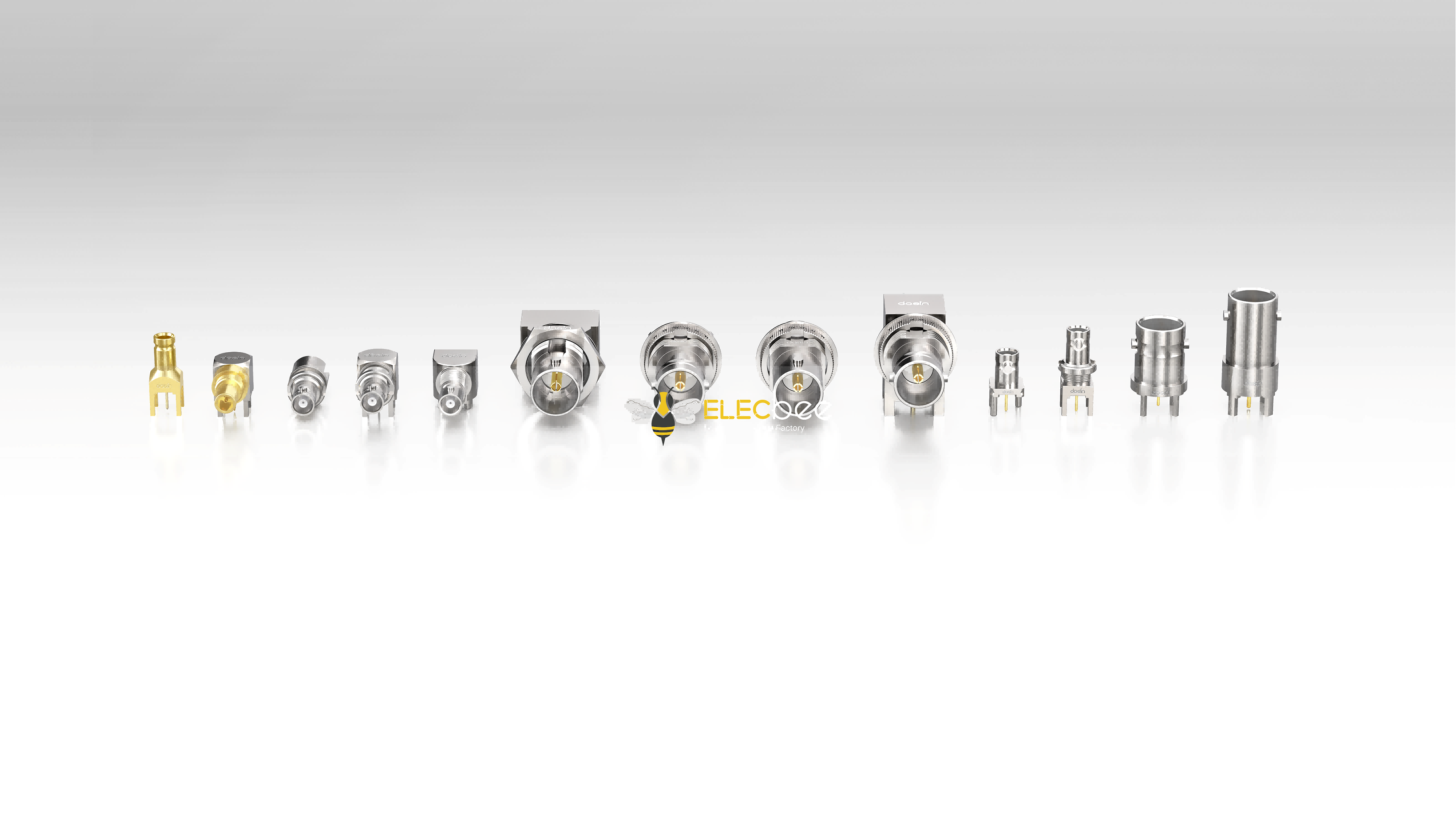 
It is commonly used in:
• Communication equipment
• Test instruments
• 5G small cells
• IoT devices
• Automotive radar systems
• Satellite and microwave systems
Choosing the wrong connector can lead to high loss, unstable matching, overheating, or premature failure.
2.Common RF Connector Types and Their Applications
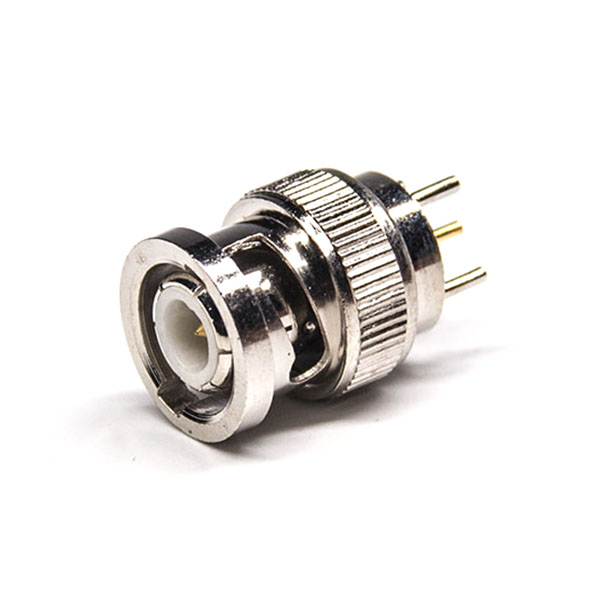
BNC
• Bayonet-lock design for quick connect/disconnect
• Common in test equipment, CCTV, broadcast equipment
• Typically supports up to ~4 GHz

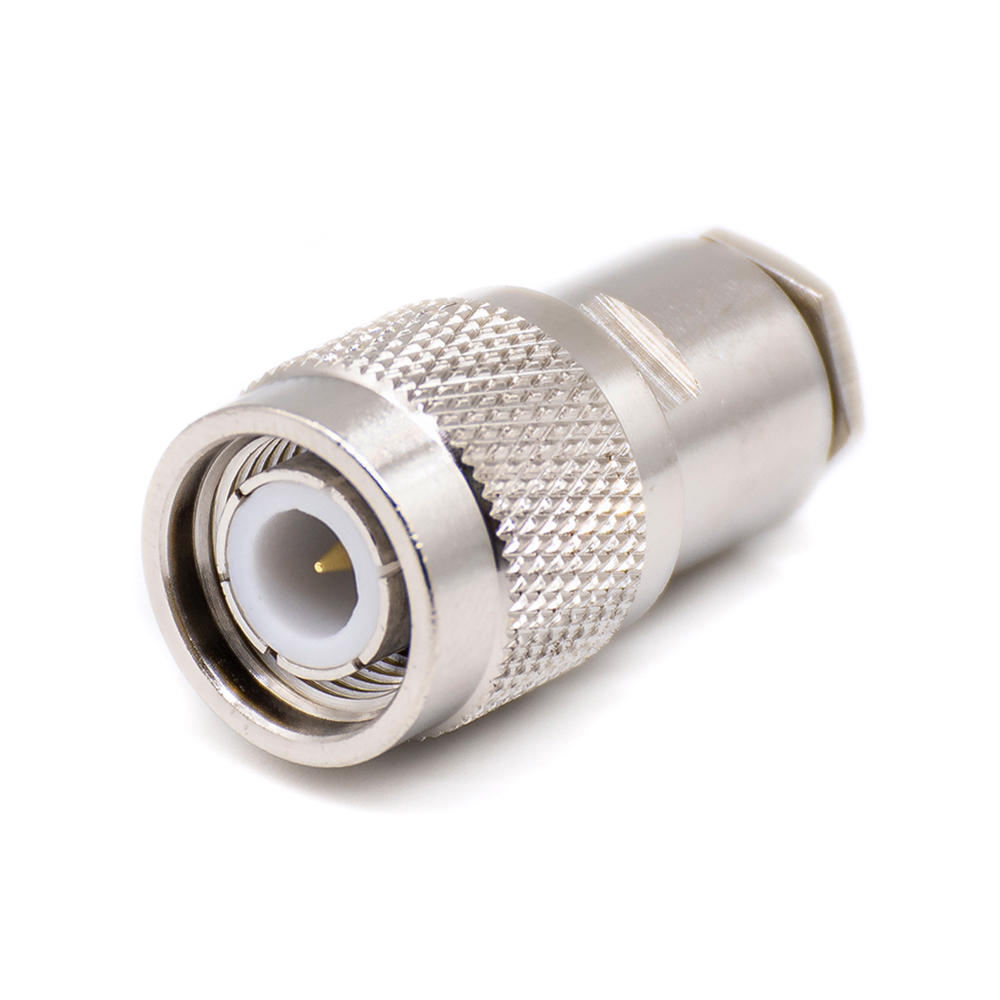
TNC
• Threaded version of BNC
• Improved vibration resistance and higher frequency capability
• Ideal for RF radios, instruments, and outdoor equipment

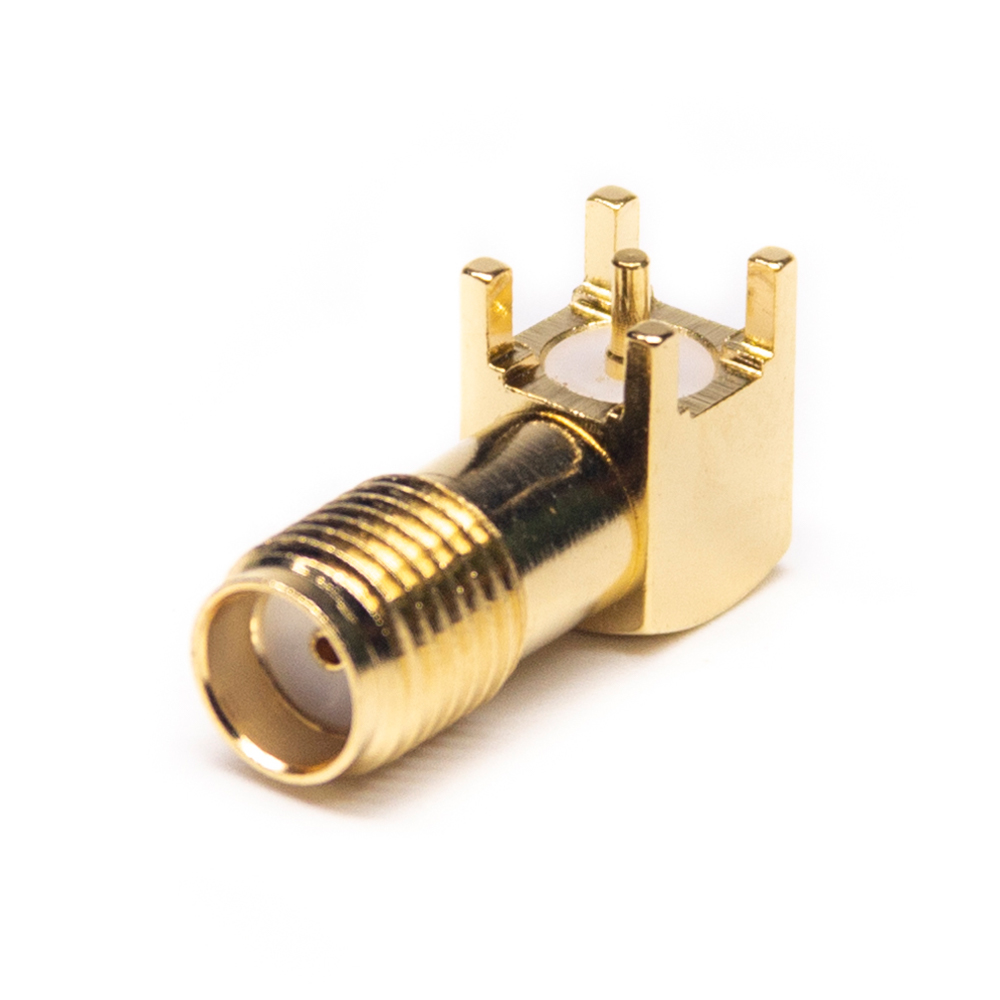
SMA
• Widely used in 5G, microwave, radar, GPS, and digital communication
• Available in 50Ω and 75Ω versions
• Frequency capability up to 18–26 GHz depending on design

SMB
• Smaller than SMA
• Snap-on design for quick mating
• Common in digital communication devices and compact equipment
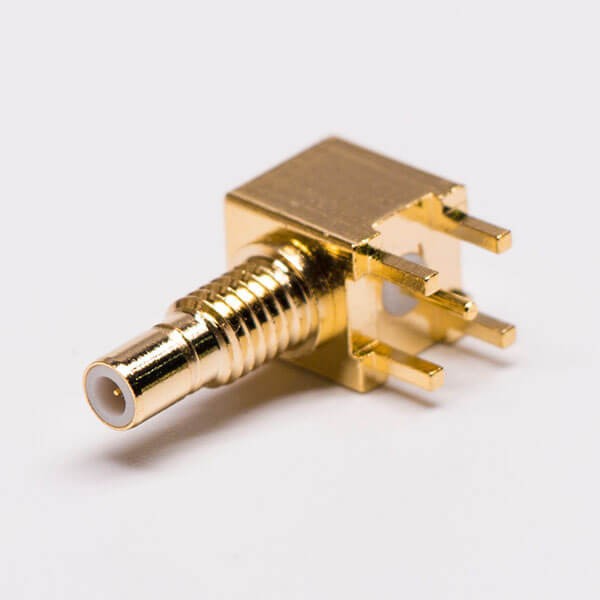

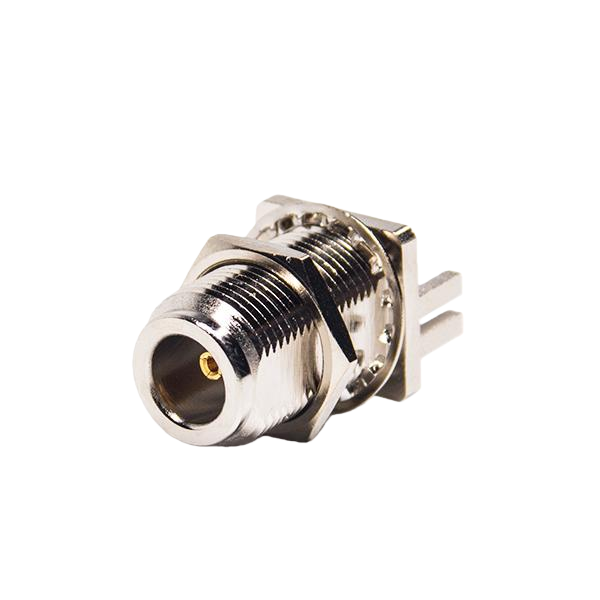
N-Type
• Rugged, weather-resistant design
• 50Ω or 75Ω impedance options
• Frequency up to 11 GHz
• Popular in base stations, test systems, and outdoor RF setups

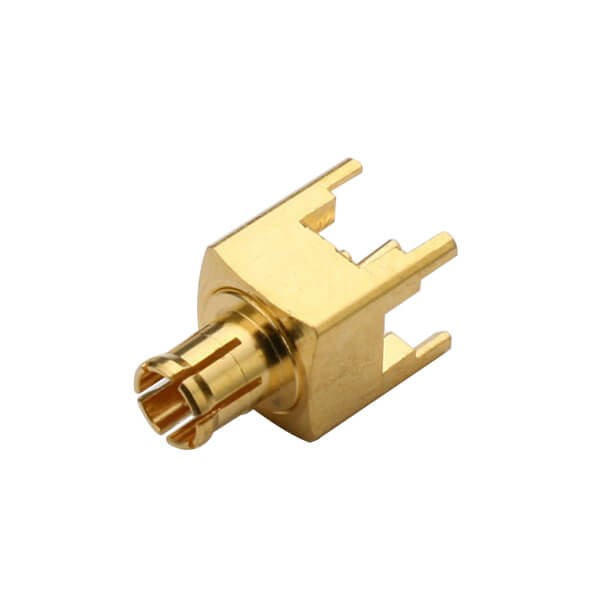
MCX / MMCX
• Very small form factor
• Suitable for compact wireless modules, embedded systems, IoT

3.Key Factors in Choosing RF Connectors
a. Impedance (50Ω vs 75Ω)
• 50Ω → RF, microwave, communication, test equipment
• 75Ω → Broadcast, CCTV, video, digital systems
Impedance mismatch leads to return loss and degraded performance.
b. Maximum Working Frequency
Each connector has a rated maximum frequency.
Example: SMA > TNC > BNC.
c. Voltage Rating
Choose connectors with a maximum withstand voltage higher than your system voltage.
4.Installation Methods
RF connectors can be installed in several ways:
Cable Terminatio
• Crimp type
• Solder type
• Clamp type
PCB Mount
• Through-hole
• Edge-mount
• Surface mount (SMD)
Panel Mount
• Flange mount
• Bulkhead (through-wall) mount
5.Materials and Plating
Connector Body Materials
• Brass → cost-effective
• Beryllium copper → high elasticity and conductivity
• Stainless steel → strongest, best durability
Plating Options
• Gold → corrosion-resistant, low loss (SMA, SMB)
• Silver → excellent conductivity but easily oxidized
• Nickel → durable and oxidation-resistant
Insulators
• PTFE (best performance)
• Polypropylene
• Polystyrene
6.How to Choose the Best RF Connector: Step-by-Step Guide
a. Determine the required frequency
○ High-frequency → SMA / N-Type
○ Medium → TNC
○ Low → BNC
b. Match impedance with your system
○ 50Ω for RF
○ 75Ω for video/digital
c. Confirm the installation type
○ Cable → Crimp/Solder
○ PCB → Edge-mount or Through-hole
○ Panel → Flange/Bulkhead
d. Check mechanical constraints
○ Compact devices → MCX/MMCX
○ High-vibration → TNC/SMA
e. Select material and plating
○ Harsh environments → stainless steel & gold plating
7.FAQ
Q1: Can a 75Ω connector be used in a 50Ω system?
It will work physically, but performance will degrade due to impedance mismatch.
Q2: Is SMA suitable for WiFi?
Yes—most WiFi modules use 50Ω SMA or RP-SMA connectors.
Q3: What’s the difference between MCX and MMCX?
MMCX is smaller and supports 360° rotation.
8.Why Choose Elecbee for RF Connectors?
Elecbee provides a wide range of high-quality RF coaxial connectors sourced from original OEM factories in China.
We offer:
• Full SMA / TNC / BNC / N-series products
• MCX / MMCX miniature connectors
• Coaxial cable assemblies
• ISO-certified quality
• 1-year warranty
If you need industrial-grade and cost-effective RF connectivity solutions, feel free to contact Elecbee anytime.








