RF connectors play a crucial role in transmitting high-frequency signals with minimal loss. Choosing the right connector type is essential for ensuring performance, stability, and compatibility in RF and microwave systems.
1.What Is an RF Connector?
An RF (Radio Frequency) connector is a type of coaxial connector used to connect cables carrying radio-frequency signals. It ensures proper impedance matching and shielding, reducing signal reflection and interference.
The connector type is often defined by the outer conductor diameter (e.g., 3.5mm, 2.4mm, 1.85mm) or by both the inner and outer conductor diameters (e.g., 7/16, 1.6/5.6 connectors).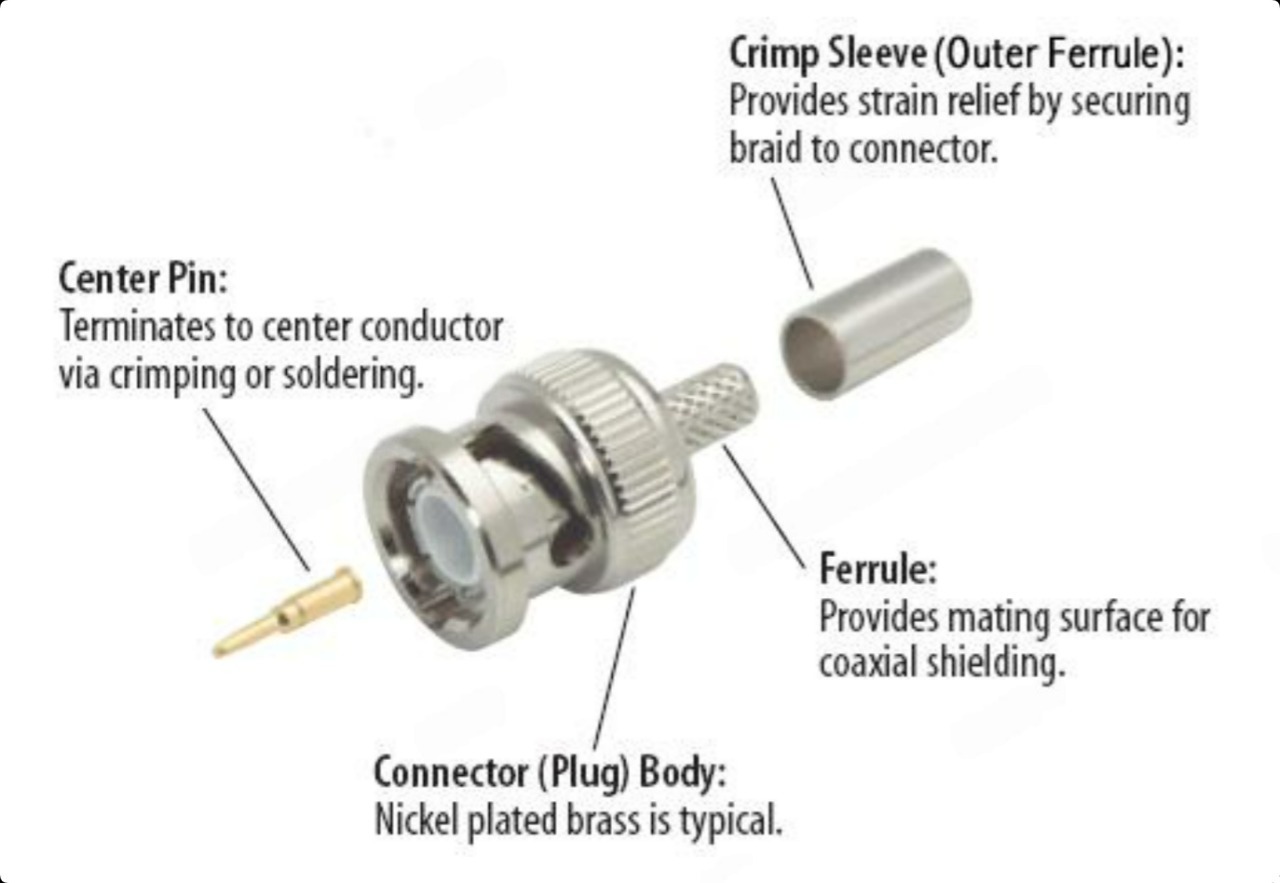
2.Common RF Connector Types and Frequency Range Chart
Below is an overview of the most common RF connectors and their frequency limits:
|
Connector Type |
Frequency Range |
Impedance |
Typical Applications |
|
BNC |
Up to 4 GHz |
50 Ω / 75 Ω |
Test equipment, CCTV |
|
SMA |
Up to 18 GHz |
50 Ω |
Antennas, Wi-Fi, lab testing |
|
N Type |
Up to 11 GHz |
50 Ω |
Telecom, base stations |
|
TNC |
Up to 11 GHz |
50 Ω |
Cellular, industrial |
|
SMB |
Up to 4 GHz |
50 Ω |
Compact devices |
|
MCX / MMCX |
Up to 6 GHz |
50 Ω |
GPS, mobile systems |
|
2.92mm (K) |
Up to 40 GHz |
50 Ω |
Microwave, 5G systems |
|
1.85mm (V) |
Up to 65 GHz |
50 Ω |
Millimeter wave testing |
3.Detailed Comparison of Popular RF Connectors
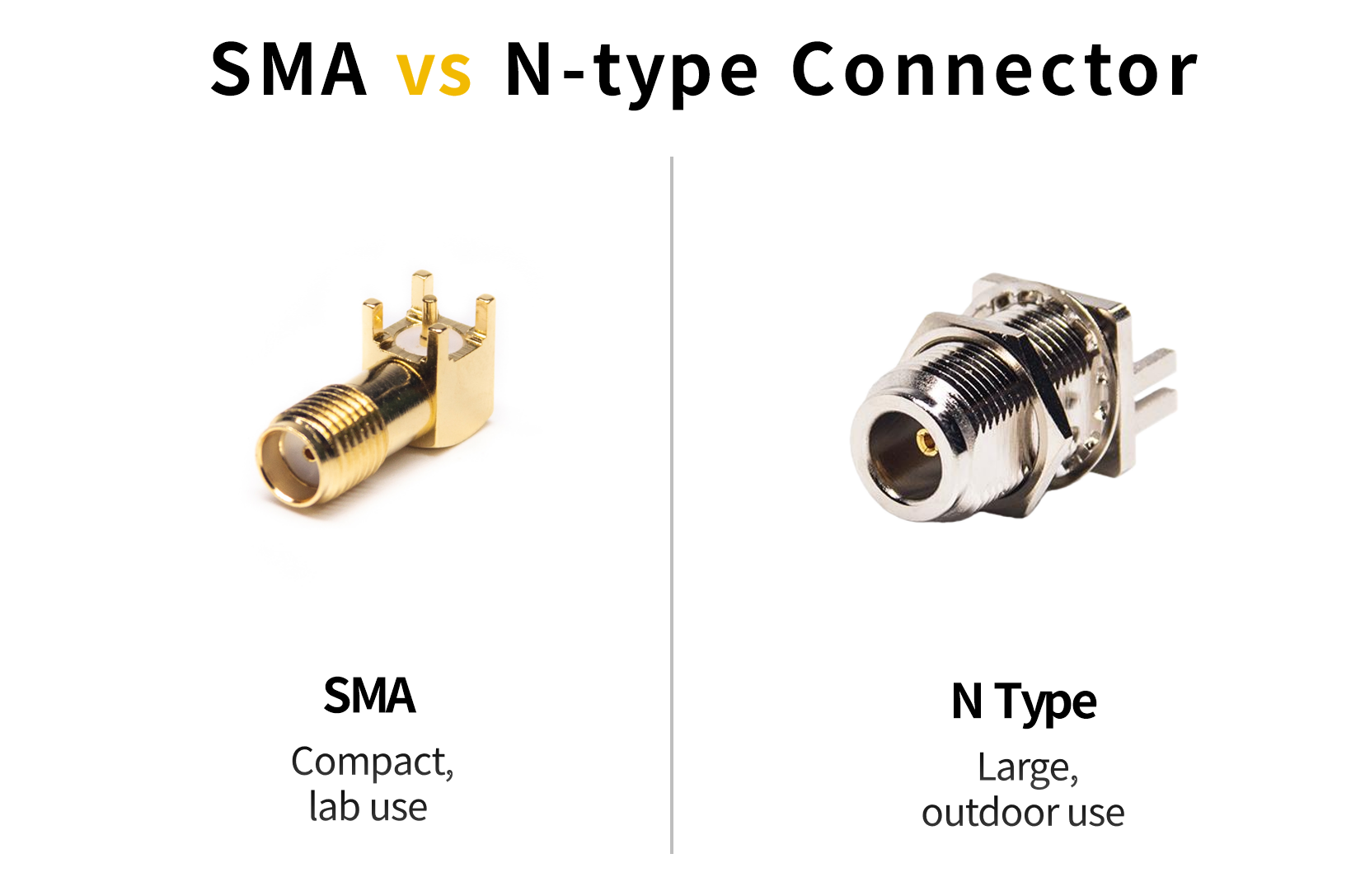
• SMA vs N Connector:
SMA connectors are compact and suitable for lab use, while N connectors are rugged and handle higher power—ideal for outdoor and telecom applications.
• BNC vs TNC:
BNC and TNC connectors share a similar design origin, but TNC uses a threaded coupling instead of a bayonet lock, offering better performance at higher frequencies.

• 1.85mm / 2.92mm (High-Frequency):
Commonly used in 5G, radar, and satellite communication systems where frequency exceeds 40 GHz.

4.How to Choose the Right RF Connector
When selecting an RF connector, consider the following factors:
a.Frequency Range: Match your connector’s frequency rating to your system’s requirements.
b.Power Handling: N and 7/16 connectors handle higher power than SMA or MCX.
c.Mechanical Size: Choose compact connectors (like SMB, MCX) for portable or embedded systems.
d.Environmental Conditions: For outdoor or industrial use, prefer waterproof or weatherproof designs.
e.Impedance Match: Ensure the connector matches your system impedance (typically 50Ω).
5.High-Frequency Connectors for 5G and Microwave Systems (2025 Update)
With the rise of 5G and millimeter-wave communication, demand for precision connectors such as 1.0mm, 1.85mm (V), and 2.4mm has surged.
These ultra-high-frequency connectors support up to 110 GHz, making them ideal for advanced testing, radar, and aerospace systems.
6.FAQ: RF Connector Compatibility and Standards
Q1: What is the difference between SMA and RP-SMA connectors?
A: RP-SMA (Reverse Polarity SMA) has reversed inner pin/gender configuration, commonly used in Wi-Fi routers.
Q2: Can I mix 50Ω and 75Ω connectors?
A: Not recommended, as impedance mismatch may cause signal reflection and loss.
Q3: Which connector type is best for 5G applications?
A: 1.85mm, 2.4mm, and 2.92mm connectors are ideal for 5G and microwave use.
Elecbee provides a wide range of RF coaxial connectors, including SMA, N, and high-frequency series.
All products are ISO-certified and come with a one-year warranty.
Browse our full RF Coaxial Connectors or RF Cable Assemblies to find the right product for your project.








